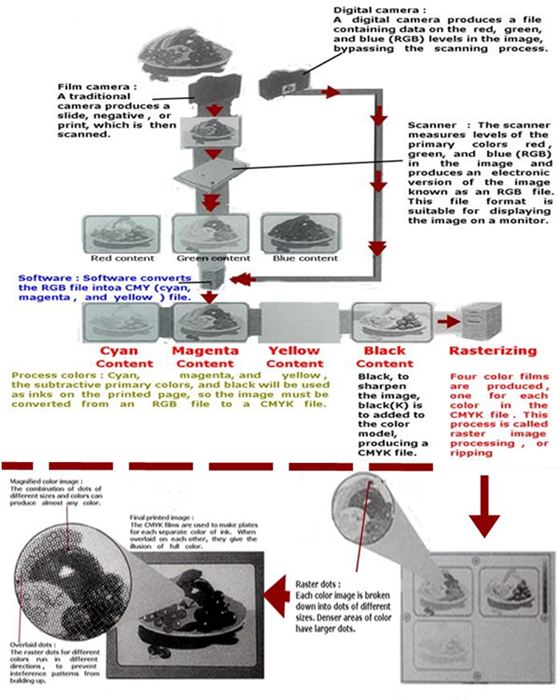
Printing
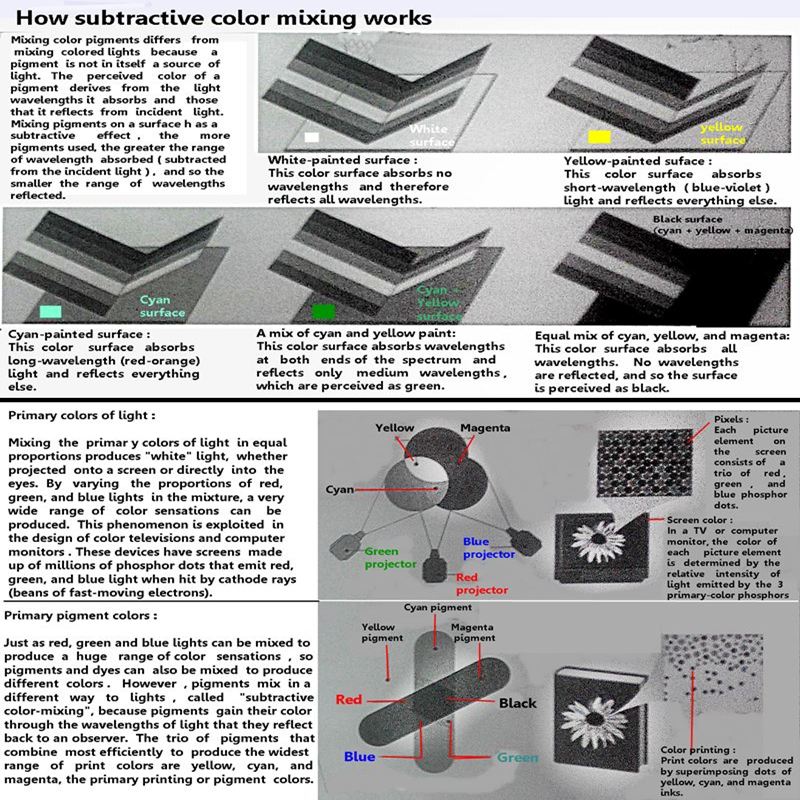
How color works
=================
Color are so familiar to us that it is easy to take them for granted. But the principles
of color mixing ,which is underlie the technology for reproducing a vast range of
colors in media such as print, photography,television, and computing , are more
complex than they might first appear. They are closely related to the way in which our
eyes and brains work together to perceive color.
The phenomenon of color derives from the fact the at light, which is a form of
electromagnetic radiation , exists in a range of wavelengths. Sunlight and other
forms of "white" light contain a mixing of these wavelengths, as can be seen by
passing a ray of such light through a glass prism. The prism disperses the light
into a continuous range, or spectrum, of colored bands of light, from red
(long wavelengths) to violet (short wavelengths).
According to the prevalent "trichromatic" theory of human color perception, the retina
of the eye contains three kinds of "cone" cells, each sensitive to a different range of
wavelengths (approximately red, green, and blue light). The sensation of any color can
be evoked by mixing lights of those three colors, the "primary colors:. Color TV works
on this principle, giving the impression of a full palette of colors using an array of red,
green, and blue phosphor dots. However, a different set of primary colors is used in
printing and photography, because colored pigments and dyes mix in a different way to
colored light.

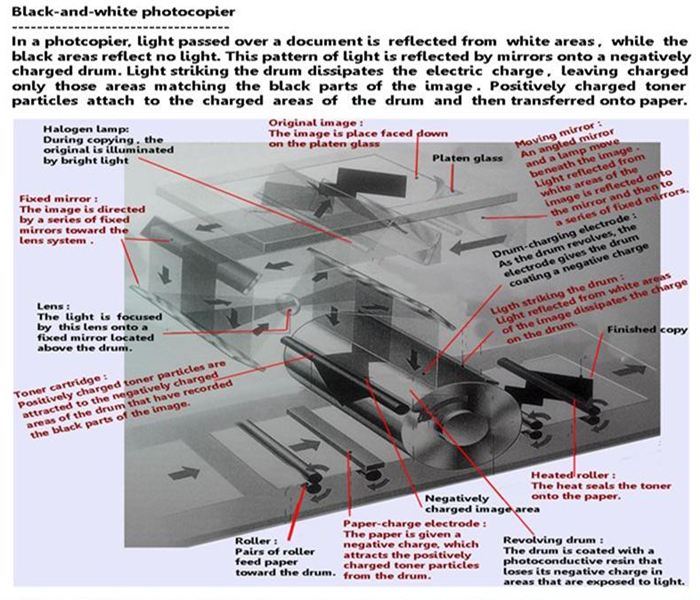
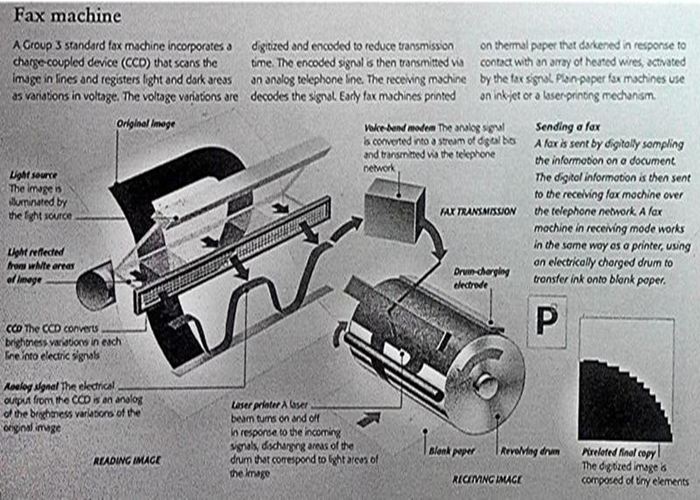
Photocopiers and Fax machines
================================
The workplace has been transformed by the introduction of modern photocopying machines
that permit multiple copies of textual and graphic material to be made quickly and cheaply.
Modern fax machines have taken this revolution one step further by allowing text and graphics
to be transmitted through the telephone network to other fax machines that reproduce the
information.
Photocopying or xerography (literally, dry copying), uses the principle of photo-conductivity,
the fact that certain substances that are relatively resistant to the passage of an electric current
become markedly more conductive when exposed to light. Photocopying a reflection of an
original image involves selectively removing an electric charge on a photo-conductive drum to
recreate the image as a pattern of charges. In order to print the recorded image, the principle
of the attraction of opposite charges is brought into play. Electrically charged paper picks up
oppositely charged toner (ink powder) that has been attracted to charged areas of the drum.
Color photocopiers use four separate ink toners : cyan, magenta, yellow, and black.
Fax (sometimes known as facsimile or telefax) technology began to be developed in the 19th century
but did not become widespread until the 1980s.Digital technology used in the Group 3 standard
fax launched in 1980 allowed the transmission of image data via ordinary telephone lines.
Preparing for print (DTP)
=======================
Today , desktop publishing (DTP) is the most popular way of producing printed material. It allows
editors and designers to produce pages quickly , alter texts and images easily, and know the
finished result will be precisely reproduced by the printer. But transforming images on a computer
monitor into ink on a printed page is a complex process, involving several steps of conversion.
The desktop publishing process has three main stages : origination , page layout, and proofing.
Origination involves commissioning text and artwork, and converting images into a digital form
using a scanner or a digital camera. Alternatively, digital artworks may be created using illustration
software. Once stored on the computer, the images may be manipulated using graphics programs
to adjust their brightness, color, contrast, etc.
Page layout is the core of desktop publishing . It uses specialized software to position and manipulate
images and text on screen . During proofing , this software also acts as an interface between the
computer and a desktop printer by converting the layout on screen into a form that the printer can
understand and use to print dots of different colors and sizes on a page. The page proofs can then be
printed , checked, and corrected.
When the page is ready , the layout program performs color separation. This process breaks down
every element on the page into the four colors used for most printing processes. The end result is a
set of color layers that will be used to make the actual printing plates.
DTP workstation :
-----------------------------
In an office DTP aetup, a scanner creates low-resolution image files called
positional-a- specialist reproduction house then creates high-quality versions of the images, which
are suitable for printing . A color printer gives a useful impression of the finished layout, but its colors
will not match those of a commercial printing press, so the reproduction house supplies color proofs
that are a closer match to the printed product.

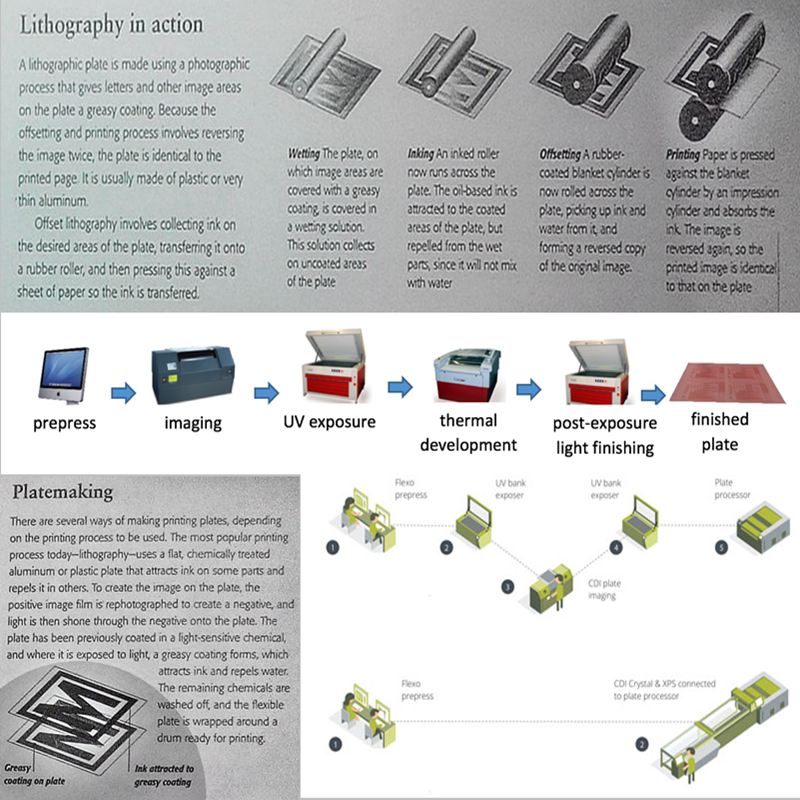
Printing (Plate-making and offset printing)
======================================
The end result of the complex preprint process is a plate for each color of ink that will appear on the
finished page. Usually, this means four plates, one each for cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks.
A wide variety of techniques can be used for transferring the image from plate to paper, but the most
commonly used is offset lithography, which relies on chemicals that attract ink and repel water.
The three methods of printing in use today are offset lithography, letterpress, and gravure. They use
different methods to collect ink on the desired areas of the plate, then transfer the ink by pressing
paper onto the plate or a transfer cylinder.
Letterpress , the oldest method of printing , uses a plate with , raised letters or patterns on it. When an
inked roller runs across the plate , ink sticks to the raised surfaces. In gravure, the letters and images
are etched into a metal plate. The ink collects in the recesses, and the surface is wiped clean before
printing.
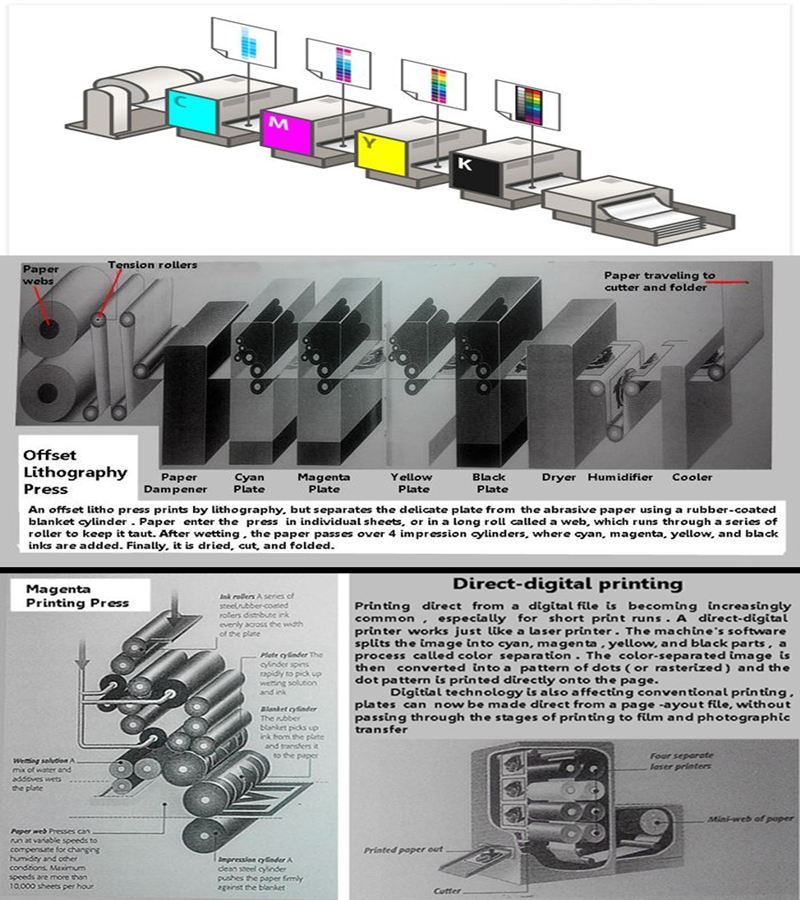
Four-color process (Separation) and Raster Image Process (Ripping)
=============================================================================