Cable Technology
Modern telecommunication relies on the accurate and rapid transmission of large
volumes of information. Cables, the original information conduit, remain central to
telecommunications networks, despite developments in satellite technology.
Advances in cable technology have led to the development of telephone trunk
cables that can be transmit tens of thousands of calls simultaneously.
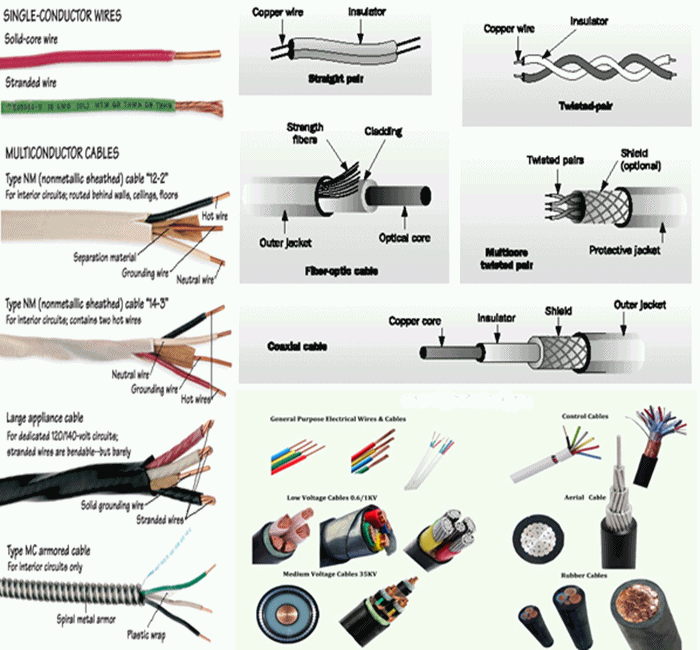
Coaxial Cable
==============
Coaxial cables have a central copper core running through the center of a cylindrical
copper braid. The two conducting channels are separated by a layer of insulation.
The inner channel carries information as modulated radio-frequency alternating
current while the outer channel gives protection against electromagnetic interference.
Coaxial cables are used in telephone, computer, and cable TV networks, and to link
TV antennae to receivers.

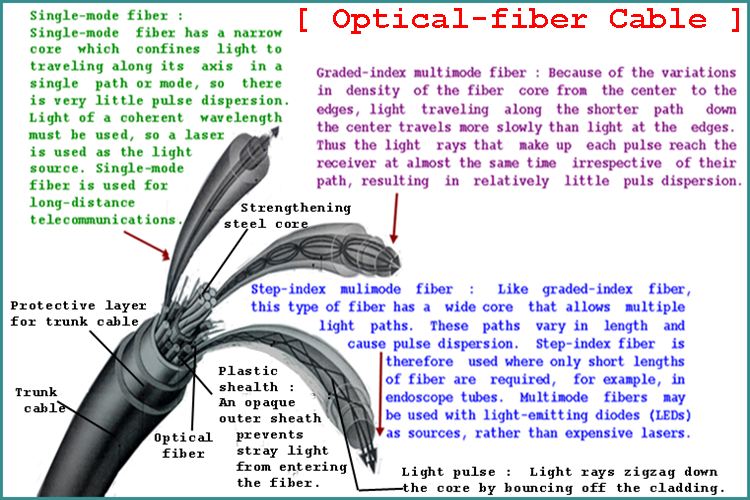
Optical-fiber Cable
=====================
Optical fibers are ahir-thin strands composed of two layers of very pure glass or plastic.
An outer cladding layer confines light signals to the inner core by a process called total
internal reflection. A plastic sheath protects the fiber from damage. Digital information
is transmitted as pulses of light. However, transmission is not flawless. Each pulse may
travel along several paths, or modes, through the fiber and tends to gradually spread out,
so a clear input pulse becomes blurred and loses intensity as it travels. This pulse
dispersion limits the rate and range of data transmission.
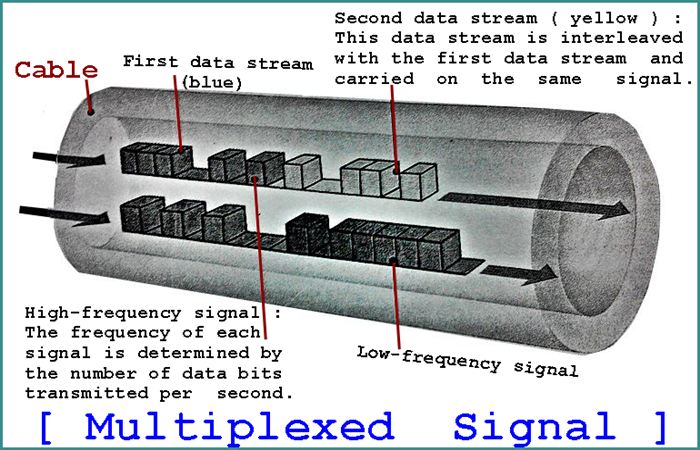
Multiplexing
==============
Multiplexing increases the capacity of cable systems by increasing the bandwidth
of each cable. Multiple data streams are sent down a single cable by combining
them to form one complex signal. Streams are then separated at the output end of
the cable. Time-division multiplexing (TDM) interleaves streams of digital data,
allowing many data streams to be sent in a fraction of the time that would be
needed to send them separately. Frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) sends
thousands of streams at different frequencies. TDM and FDM can be used together
to maximize cable bandwidth.
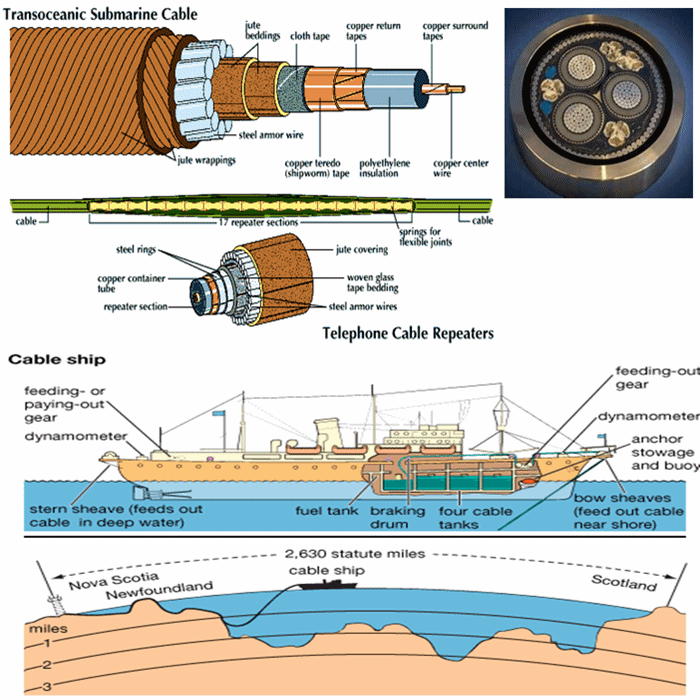
Transoceanic Cables
======================
Communication over long distances is achieved by the transmission of data as
waves or streams of pulses. An electric current alternating (switching direction )
at radio wave frequency is modulated (shaped) by an analogy or digital data signal.
The modulated wave is sent through coaxial cables, or broadcast via ground-stations
and satellites as radio waves. Digital information may also be sent as streams of
light pulses (or, less commonly, of electric pulses), a pulse representing as "1" ,
and the absence of a pulse representing a "0". Cables act as highways for these
data streams, and must be designed to minimize interference between different
data streams, which leads to loss of data. The bandwidth of a cable is a measure
of the amount of data that can transmit. Optical fibers have a greater bandwidth
than coaxial cables, and can transmit signals farther and faster since light is less
prone to attenuation (power loss) than electric currents, and propagates faster.
The bandwidth of a cable system can be increased by installing more cables, but
also by employing multiplexing techniques, which squeeze more data down each
cable.