Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is potentially a huge source of cheap energy. Unlike conventional
power station, nuclear rectors do not rely on burning fossil fuels. Instead, they split
apart individual atoms of the metal uranium , releasing huge amounts of energy in
the process. In theory, nuclear power could generate far more energy than the
world's remaining fossil fuel reserves, but the cost of building reactors, and the
dangerous waste they produce , have held it back.
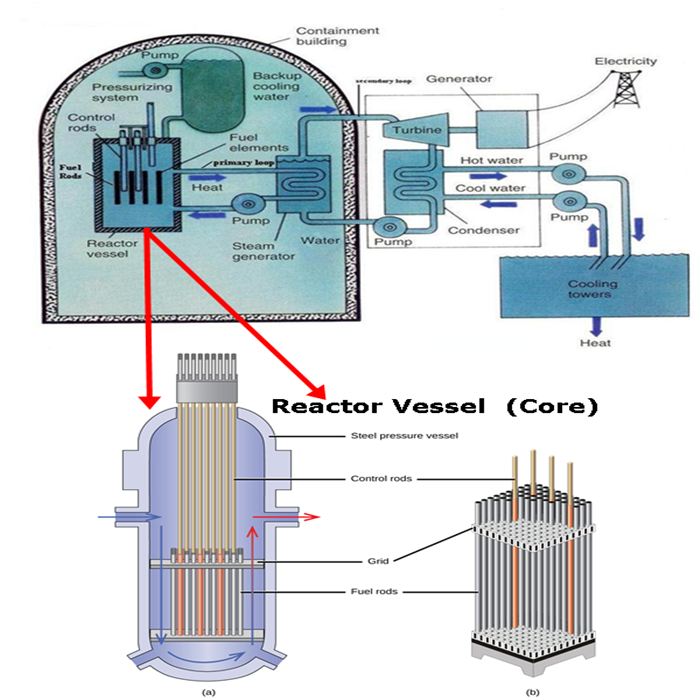
Nuclear Fission and Pressurized Water Reactor
=========================================
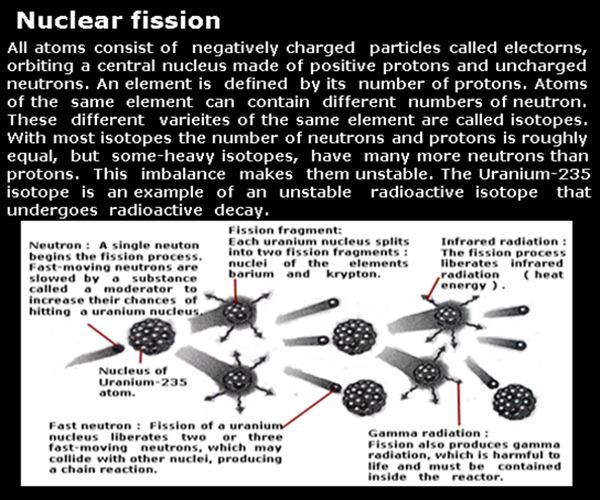
Radioactivity is widespread in nature, the atoms of substances such as uranium
have naturally unstable nuclei that spontaneously split apart, decaying into two
lighter elements and releasing energy ( a process called fission ). Nuclear reactors
are designed to produce fission on demand in a controlled chain reaction in which
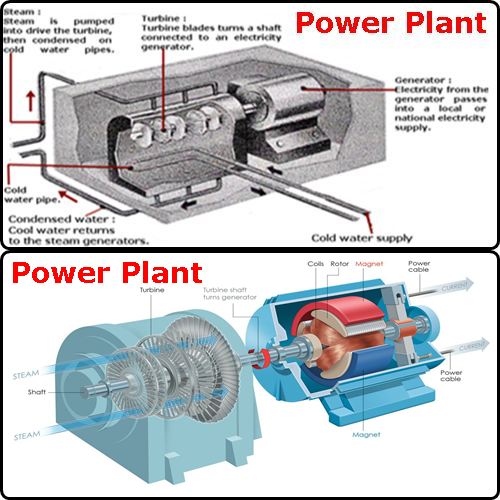
the products of the reaction tend to make it continue. Heat released during the
reaction is used to boil water and produce steam, which spins turbines to generate
electricity, in the same way as a conventional power station.
Reactor Defueling
======================
To achieve fission, a sub-atomic particle called a neutron is fired at a uranium atom,
causing the nucleus to split. This releases energy and more neutrons, which in turn hit
the nuclei of nearby atoms and set off a chain reaction. Harmful radiation is released
along with enormous heat, so nuclear power stations must contain this radiation and
control the speed of the reaction. The smaller nuclei produced during fission are also
often highly radioactive, so nuclear waste is dangerous and must also be handled
carefully.

In the future , nuclear fission may be abandoned in favor of a cleaner and even more
powerful source of energy, nuclear fusion, the process powers the Sun. In a fusion
reaction, nuclei of hydrogen, the lightest element, are forced together to make heavier
elements, releasing energy in the process. However, this energy is difficult to harness
because of the enormous temperatures and pressures needed to produce fusion.
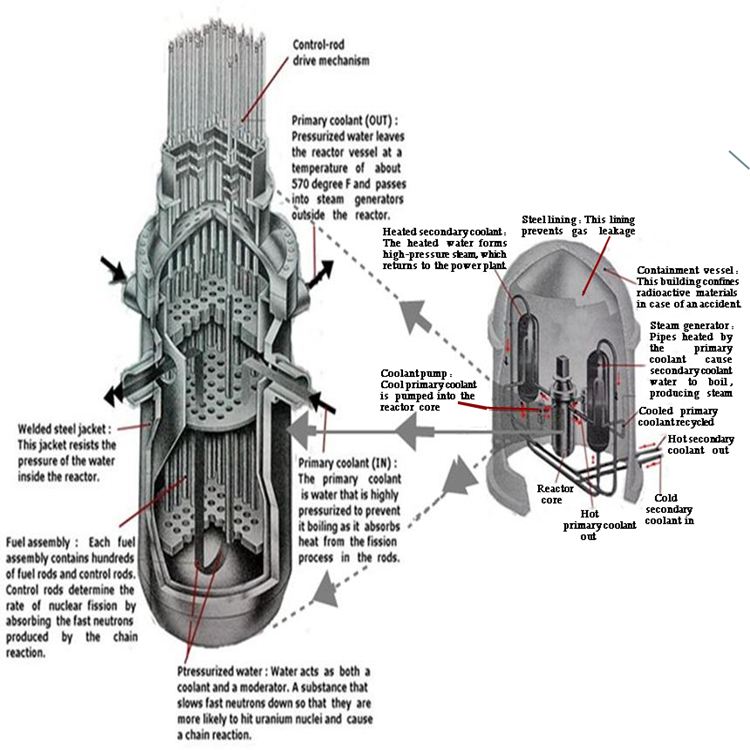
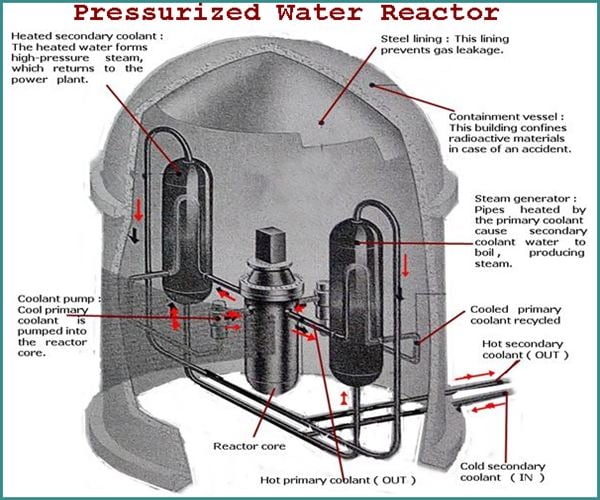
Harnessing Nuclear Power , Pressurized Water Reactor and Power Plant
===========================================================
More than two-thirds of the world's nuclear power stations contain the process of
nuclear fission inside pressurized water reactors. In these reactors, water is used
to moderate the speed of neutrons that are released from uranium nuclei. The heat
energy released by fission heats the water to produce steam, which drives a turbine
linked to electricity generators.